Research
Breathing motion and spiral arms
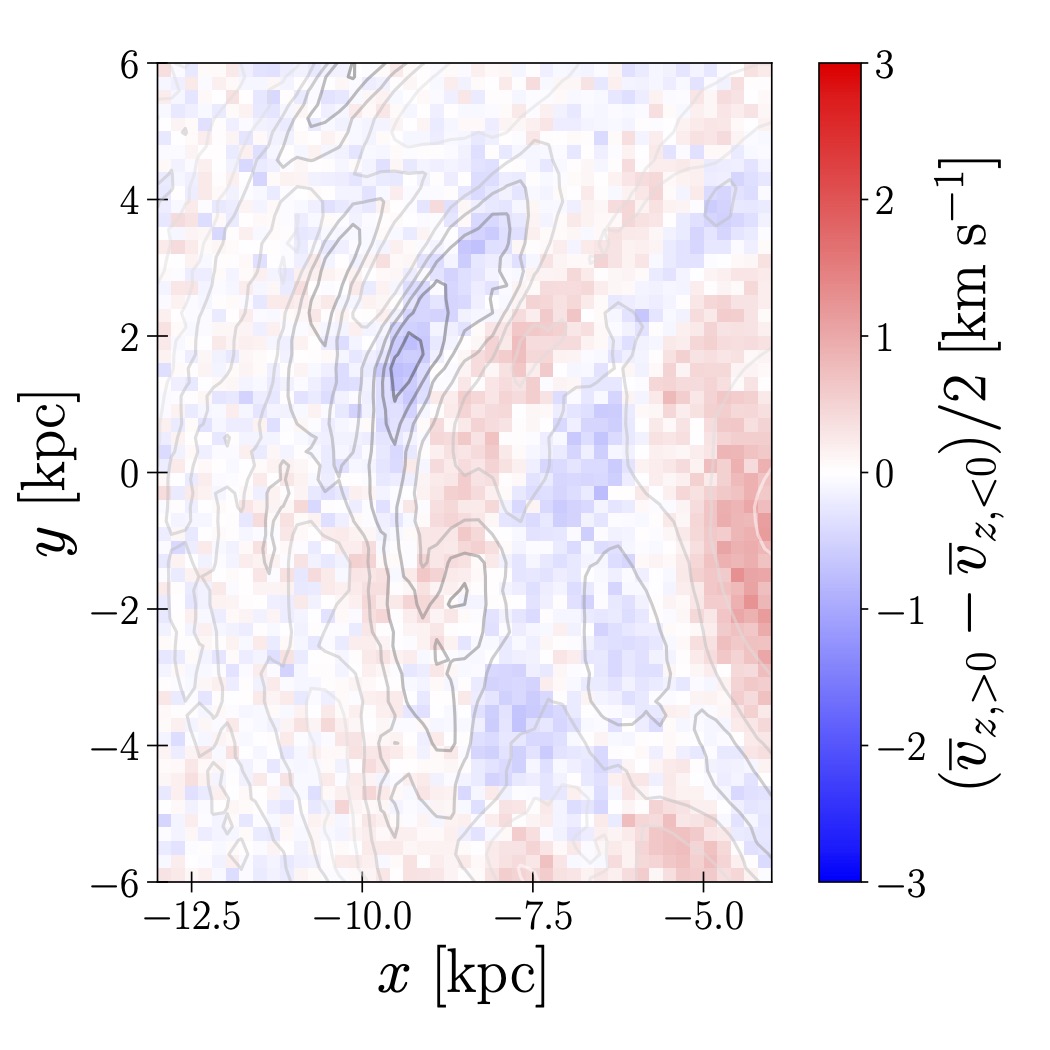
Gaia DR3 data reveals a distinct pattern of compressing breathing motion a coherent, antisymmetric vertical motion of stars around the Milky Way's mid-plane aligned with the Local arm. Comparison with an N-body simulation suggests that this pattern indicates the Local arm is in a growth phase, while the expanding breathing motion observed near the Perseus arm may indicate it is in a disruption phase. These findings suggest that the Milky Way harbours dynamic spiral arms in various evolutionary phases.
Read moreBar resonances
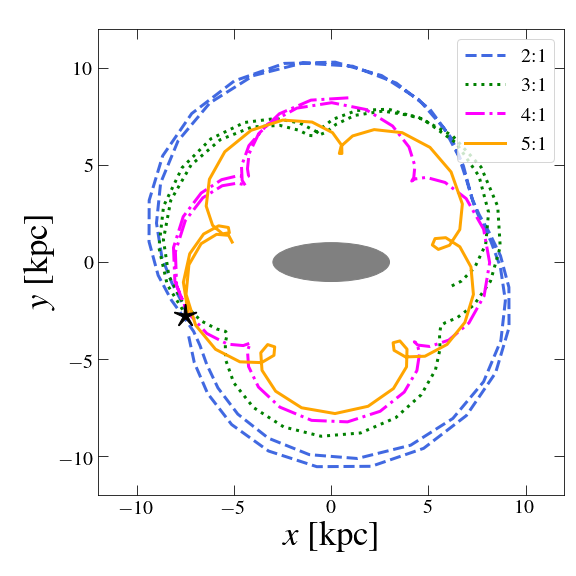
The Gaia data reveal complex stellar velocity-space structures, such as the Hercules stream, which cannot be explained by axisymmetric models. Using an N-body simulation of a Milky Way-like galaxy, Asano et al. (2020, 2022) demonstrated that these substructures, including the Hercules stream, arise from bar resonances. We employed the Kullback-Leibler divergence to analyze the spatial and temporal variations of velocity-space distributions, finding that Hercules-like substructures are most prominent in specific regions in the bar's rotating frame, highlighting the dynamic influence of bar resonances on the stellar distribution.
Read moreSagittarius dwarf impact and phase spirals
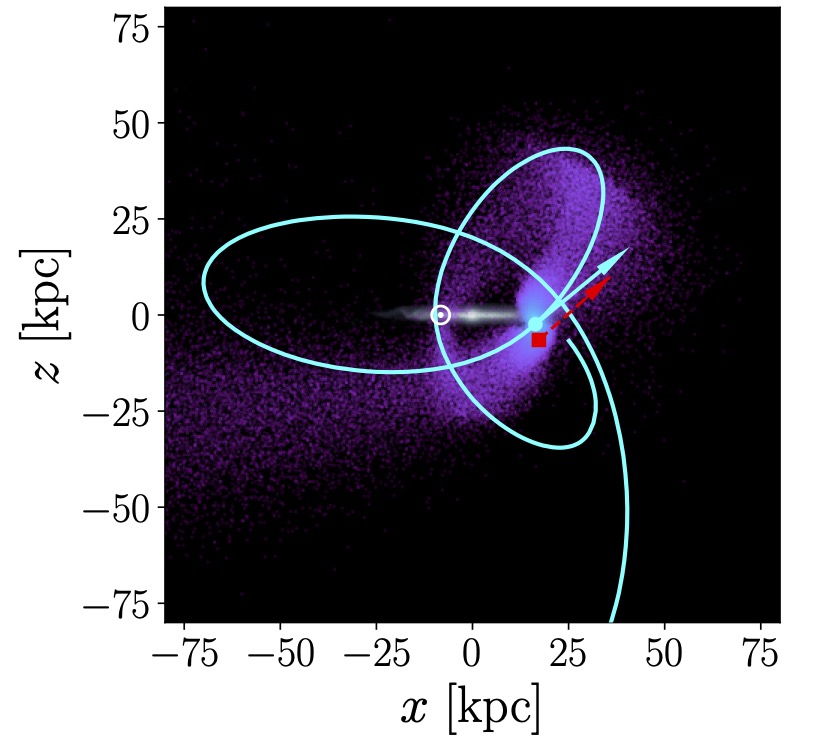
We investigated the excitation and evolution of the bending mode (one-arm phase spiral) and the breathing mode (two-arm phase spiral) using high-resolution N-body simulations of the MW-Sagittarius dwarf interaction. We show that the satellite directly excites the bending mode while inducing spiral arms that drive the breathing mode. The bending mode quickly decays due to horizontal mixing, while the breathing mode persists, sustained by spiral arms, resulting in a transition from bending-dominated to breathing-dominated state. The simulations reproduce one-arm phase spirals in the solar neighborhood and two-arm phase spirals in the inner galaxy. This study emphasizes the interplay between direct and indirect processes in Milky Way's vertical dynamics.
Read more